Chapter 3
How does BandChain work
Estimated time: 20 mins
Yoda
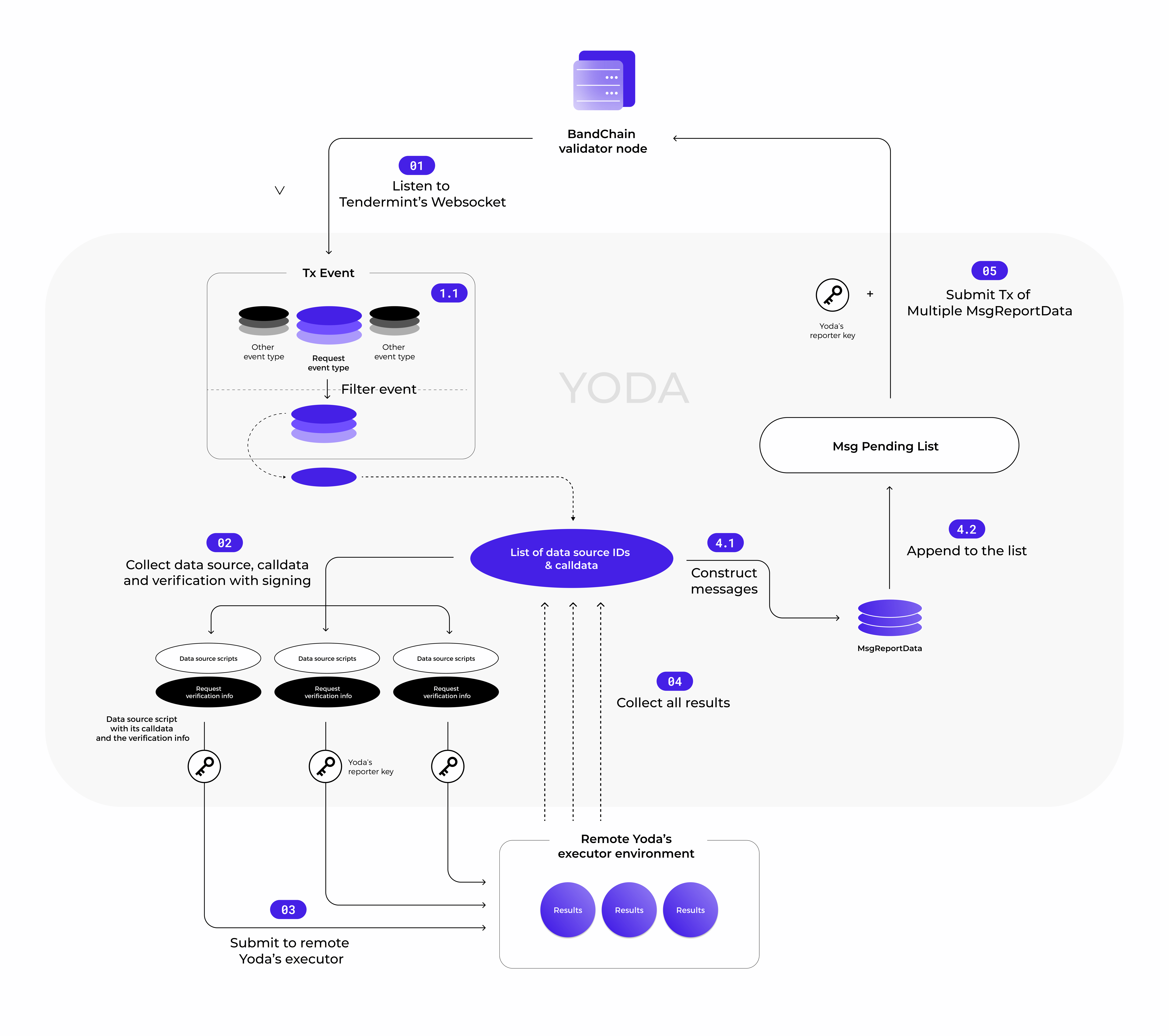
Yoda is a program that BandChain's validator nodes use to fulfill data requests when they're selected to do so.
Yoda's main job is to listen for incoming data requests on BandChain and to execute the corresponding data sources listed within the data request. Once the data source is executed and its results received and parsed, the end-results are then collated and packaged into a MsgReportData, stored in a local pending list then broadcasted onto BandChain.
Data Sources
A data source is the most fundamental unit in BandChain's data system. It describes a procedure, like a Python script, to retrieve and process a raw data point from an external source.
Anyone is able to deploy and register a data source on BandChain by sending a MsgCreateDataSource message to BandChain and if an owner is specified, the owner is able to edit a data source by sending a MsgEditDataSource message to BandChain.
Data Scripts
A data script is a turing-complete executable program that is at the heart of BandChain. It encodes a set of raw data requests, which is then sent to the data sources, and aggregates the raw data returned from the data sources into a final report.
When a data script is called and executed, a data proof is also produced. This proof is a Merkle proof that shows the existence of the final result of the data request on BandChain. In addition to the actual result of the request, the proof also contains information on the request parameters such as the script hash, the time of execution and the number of validators that responded. This proof can then be used by any smart contract on other blockchains to verify that the existence of the data on BandChain and to retrieve the results stored.
Similarly to a data source, anyone is able to deploy or edit a data script on BandChain by sending a MsgCreateOracleScript or MsgEditDataSource message to BandChain.
Prepare Phase
During the preparation phase, a data script is used to request external data from validators through yoda.
Execution Phase
In the execution phase, a data script processes the data reported by validators and generates an output. Although there are various methods for data script processing, a frequently employed technique involves medianizing the results.
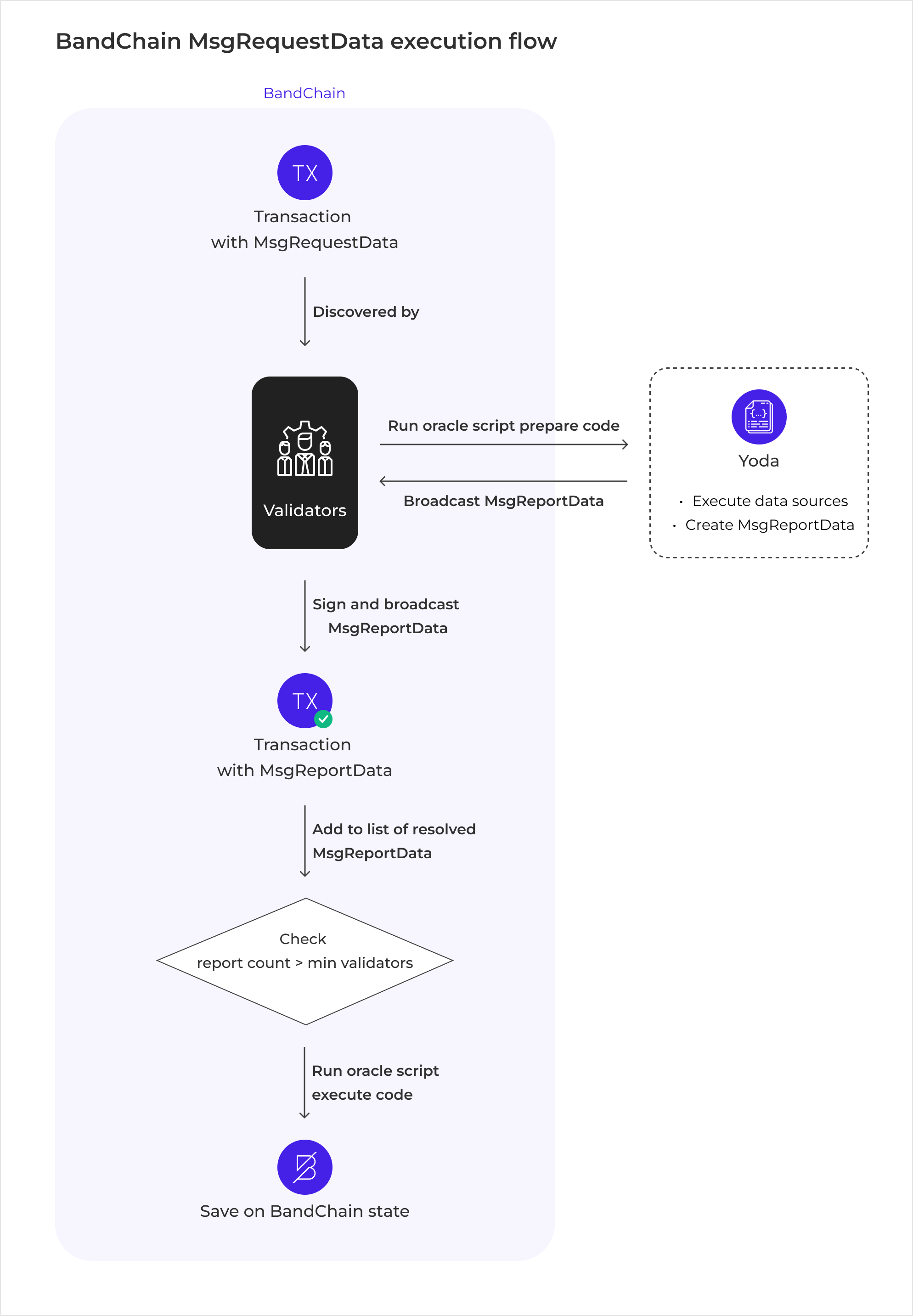
Data Request Flow
- When requesting a data script, a
MsgRequestDataneeds to be broadcasted in a transaction to BandChain. - Once the transaction has been discovered on-chain, the randomly selected validators will then run the data scripts prepare code.
- The prepare code sends a request to Yoda, which will execute the associated data sources and create a
MsgReportDatacontaining the data sources results. - The
MsgReportDatais then broadcasted in a message signed by the validator and broadcasted. - Once the transaction containing the
MsgReportDatais delivered, the reports are then checked to assure that the minimum number of validators have reported the data and once that is assured, the request is added to thePendingResolveList. - At the end of the block, the data script execute code is then run and its results saved on-chain.